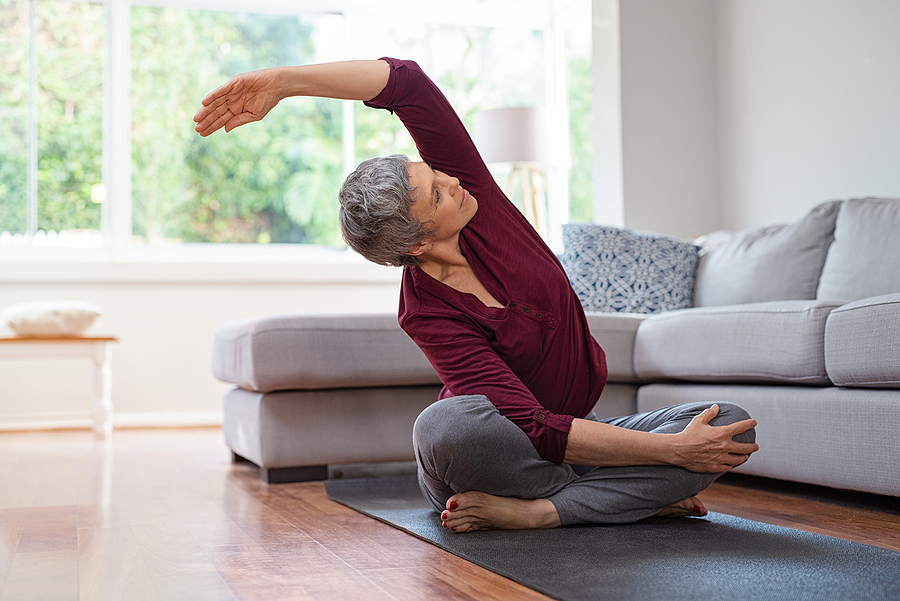
What is a muscle strain? It’s an injury to a muscle or the tendon that connects a muscle to a bone. It can indicate the fibrous tissue has been stretched farther than it should, creating a partial (minor) tear or a complete tear. Either way, treating muscle strains is important to prevent further injury.
Several things can cause muscle strain, and they all come back to either a muscle being stretched too far or forced to contract harder than is normal. Once this happens, there are three grades of strains:
- Grade I – Mild strain with stretched muscle fibers and possibly a few torn strands. It’s painful, but the muscle strength isn’t impacted.
- Grade II – Moderate strain with several torn fibers. Pain is more severe, and swelling is common. You might even see a bruise. Muscle strength is impacted.
- Grade II – The muscle is completely torn in half or rips away from the tendon. Loss of muscle function, pain, swelling, and bruising is common. A pop is often felt as the muscle separates.
As soon as muscle strain occurs, stop and take care of yourself. Grade 1 muscle strain is something you can usually treat with self-care. Grade 2 and 3 should be treated by a doctor. You do not want to cause further damage. Premium Sports & Orthopedics has tips to help you better understand what to do now.
What Muscles Are Most Likely to Be Strained?
Pulled muscles can happen anywhere, but these muscles make up the majority of injuries treated by doctors.
- Hamstrings – Muscles going from the hips to the knees on the back of the thigh.
- Hip Adductors – Muscles around the groin to the hips.
- Gastrocnemius – Calf muscle that goes from the knee to the ankle.
- Quadriceps – Muscles going from the hips to the knees on the front of the thigh.
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation Equals RICE: Do This First
RICE is the abbreviation of Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation, and it’s the first thing to do when you experience muscle strain. Here’s what it means.
- Rest – Stop using that muscle as much as you can.
- Ice – Put an ice pack on the muscle. A towel can help direct exposure to the ice that damages the skin.
- Compression – Use compression bandages to reduce swelling.
- Elevation – As much as you can, keep that muscle elevated.
Some of that guidance depends on what muscle is strained. If it’s an ankle, elevating it is easy. If you strain your shoulder muscle, it’s harder to keep that elevated. You may find it hard to follow all of the steps of RICE but do your best.
You also need to use common sense when deciding if it’s time to see a doctor. If the pain is severe, there’s a lot of discoloration, or you noticed there’s a clear separation where there used to be muscle, call a sports and orthopedics specialist immediately to get an appointment.
Don’t Try to Suffer Through the Pain
Don’t deal with the pain. If you’re in a game. Stop playing before you cause damage that requires surgical repair. You can support your team from the sidelines while taking the time you need to heal.
An over-the-counter NSAID like ibuprofen helps ease the pain and also helps with inflammation. Ask about alternating ibuprofen and acetaminophen to ease severe pain.
Tips for Preventing Muscle Strain
Before any activity, including a hike, game, or practice, make sure you complete a warm-up. You don’t want to jump right into the action without giving your muscles time to loosen up.
When you’re exercising, make sure you maintain the correct form. This is why it’s valuable to work with a personal trainer or physical therapist, especially if you’ve experienced injuries in the past or are out of shape. It’s better to strengthen muscles slowly and correctly that push too hard and do damage.
Make sure you sit and stand with proper posture. Keep your spine straight, don’t slouch, and stand in ways that properly support your joints and muscles without putting more weight on one area than another.
Obesity puts a lot of extra strain on the muscles in the legs and back. If you are overweight, work with a doctor on a plan that helps you get to a healthier weight, which will lessen the strain on your muscles.
Eat a healthy diet. You may not tie the foods you eat to muscle strain, but muscle strength and repair require a lot of protein. The recommended daily allowance is 0.8 grams per 2.2 pounds of body weight. One study found that 46% of older adults didn’t eat enough protein. Make sure you are. If you weigh 200 pounds, you should be eating around 72 grams of protein each day. Here are several popular foods and the protein content in each one.
- ½ cup of cooked lentils – 9 grams
- 1 cup of almond milk – 1 gram
- 1 cup of milk – 8 grams
- 1 cup of soy milk – 7 grams
- 1 ounce of beef, chicken, lamb, pork, or turkey – 7 grams
- 1 ounce of crab, lobster, or shrimp – 6 grams
- 1 ounce of fish – 7 grams
- 1 ounce of tofu – 3 grams
- 2 tablespoons of peanut butter – 7 grams
- An egg – 6 grams
Finally, lifting heavy items is another common reason for muscle strain to occur. Always lift from the legs. Don’t bend over and put the force of the item’s weight on your back. If something is too heavy, ask someone else to help.
If you’re doing some more intense yard work, stop and take breaks often. Don’t overexert. Know your limits, too. If something is causing pain, stop and get someone to help out.
The same is true for activities like hiking. If you’re starting to feel pain, you’ve pushed too hard. Don’t try to continue as that could create damage that requires medical care and leaves you stranded until rescuers can get to you. Go back and rest up for another day.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Make an appointment at Premium Sports & Orthopedics if the pain is severe. If you cannot move the muscle, feel a pop when the injury happens, or experience swelling that isn’t going away, it’s important to see a doctor.
Don’t hope for the best. If your muscle doesn’t heal properly, repeat injury is a real risk. You might experience a complete tear next time that requires surgery and needs months to recover. It’s important to have muscle strain properly diagnosed and treated.
Surgery may be needed for severely torn muscles, but you can treat other muscle strain injuries with physical therapy, massage therapy, stem cell injections, and PRP injections. Working with the orthopedic team at Premium Sports & Orthopedics ensures you heal correctly and avoid reinjury.