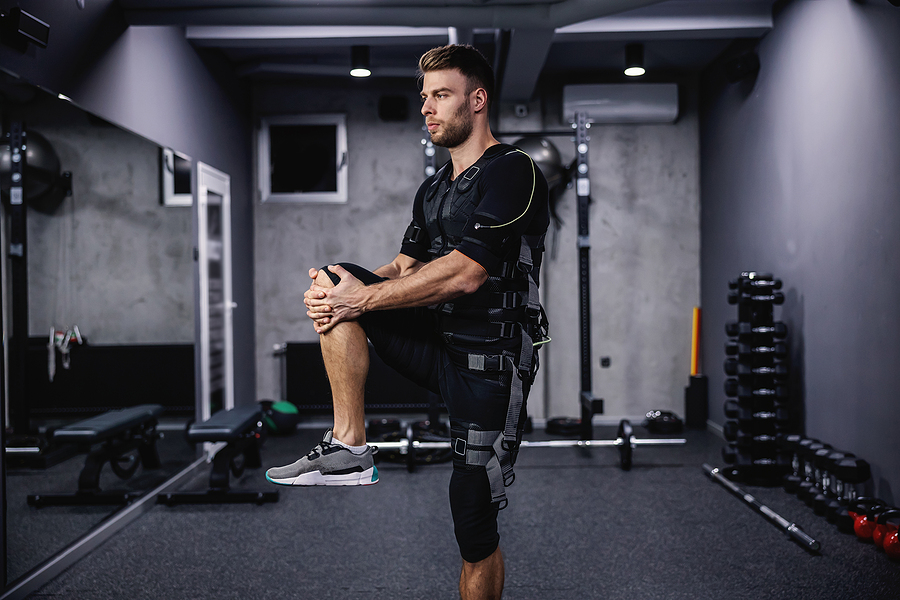
When you exercise, your nervous system sends electrical pulses to your muscles to cause the contractions and create force. Your muscles and nervous system work together to coordinate your movements and improve your physical reactions.
When you add electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), the electrical pulses trigger contractions. It makes it possible to improve muscle tone and increase muscle strength in less time. EMS also helps target specific muscle groups that your workouts may be missing. It also helps reduce pain and improve circulation. With more oxygen and essential nutrients going to the muscles, muscles recover faster.
When you’re an athlete, EMS is one of the best ways to reduce injuries. Premium Sports & Orthopedics explores how EMS works and why it’s one of the best ways to lower your risk of an injury during a practice, scrimmage, or game.
Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Electrical Muscle Stimulation
EMS stands for electrical muscle stimulation. It’s a way to target specific muscle groups to help strengthen them, even if those muscles are typically hard to focus on. It works like this.
- Wear a specially-designed suit and leg straps that contain many electrodes.
- Follow a workout routine under the doctor’s guidance.
- Electrical impulses are delivered to different muscle groups as you move.
- Muscles contract with more intensity with the combination of movement and electrical stimulation.
Because the electrical pulses are making muscles contract, muscles tone without the need for excessive weights, which is better for your joints. Body shaping and weight loss occur faster. All of this takes just 20 minutes per session, once or twice a week.
EMS Aids Balance and Stamina
One of the problems with a general workout is that you may be missing out on weaker muscle groups. Sometimes, one muscle gets more of a workout than another, and that can throw you off. Your biceps may develop well, but not every muscle surrounding your rotator cuff strengthens at the same time.
EMS is designed to strengthen muscle groups equally. As a result, you eliminate having a weaker muscle group, which impacts balance or stamina. When you have strong muscles that are supported by weaker muscles, the distribution of force becomes imbalanced. That puts stress on your joints, ligaments, and tendons, which leads to injuries during a game or practice.
It’s essential that a workout targets all muscle groups. Plus, EMS helps with oxygen and nutrient flow by improving circulation. With an EMS workout, it may feel like you’ve exercised more than normal, and most people say their muscles are sore the next day. Listen to your doctor for how to manage the post-workout recovery. Don’t let it keep you from additional EMS workouts. The outcome is worth a bit of muscle soreness.
What Do Research and Real-World Examples of EMS Workouts Show?
In a recent study, 14 men and 14 women were recruited to explore the benefits of EMS training. The men and women were split into groups of seven participants each and grouped by weight, height, and gender. Two groups underwent EMS training, while the other groups completed resistance training focusing on the abs, arms, back, and legs.
Groups that did daily EMS saw significant increases in muscle mass and lowered body fat. All groups experienced the same levels of fatigue. More importantly, muscle mass in those not doing EMS workouts saw a slight decline (28.8 kg to 28.6 kg), while daily EMS sessions saw muscle mass increase (29.5 kg to 30.3 kg).
Usain Bolt is one of the many athletes who embraced EMS training to improve performance and reduce the risk of injury. It’s reported that Bolt kept developing injuries when he tried weight lifting. He turned to EMS workouts for core strengthening that wouldn’t harm his joints. He improves his power and speed without causing injury.
For his role in Spider-Man, actor Tom Holland turned to EMS training to develop the muscles needed for the action role. He admits he hurt 12 hours after his first training session, but the improvements in muscle tone and stamina were impressive.
Celebrities around the world use EMS for heightened performance without risk of injury. EMS is helpful in the following ways.
- Endurance sports – Helps avoid overuse injuries and fatigue in events like marathons and triathlons.
- Sports where objects are propelled or thrown – Helps avoid common injuries like rotator cuff injuries that occur with repetitive over-the-head motions, such as happens in baseball, tennis, and volleyball.
- Sports where you jump and land frequently – Helps strengthen lower leg and upper leg muscles to absorb the shock from the impact during a landing, such as basketball, football, and gymnastics.
Integrating EMS Training Into Your Injury Prevention Program
EMS is a great way for athletes to avoid injury, but it should be part of an injury prevention program and not the only step you take. We have a few suggestions on other things to incorporate into injury prevention programs.
The foods you eat help fuel your body. Grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins are important. You don’t want to rely on processed foods that have excessive amounts of sugar and saturated fats. They don’t help your body heal and recover after a game or an intense workout.
Make sure you’re getting enough sleep. Your body heals and recovers while you’re sleeping, so if you’re only taking quick naps here and there, you’re not giving your body enough time to recover after a workout or game. Ideally, aim for seven to eight hours of sleep each night.
Prevent Injuries Using EMS Under Expert Guidance
EMS training is an excellent way to prevent injuries on the field or court, but it’s also helpful in getting back into shape after a long break or if you’ve gained weight and need to lose weight before the season starts up.
It’s not the right training program for everyone. If you are pregnant or wear a pacemaker, EMS isn’t advised. It’s also not a program you can do at home. You must see a sports and orthopedics doctor who is knowledgeable in EMS workouts in order to exercise safely and correctly.
Much of the program is dependent on your fitness level, information on past injuries, and the sports you play. A doctor discusses your goals and the position you play before customizing an EMS workout for you.
That’s why it’s essential that you work with an expert in EMS. Premium Sports and Orthopedics helps athletes avoid injuries, restore muscle strength after previous injuries, and get in shape for upcoming sports seasons. Reach us online to make an appointment for EMS training.